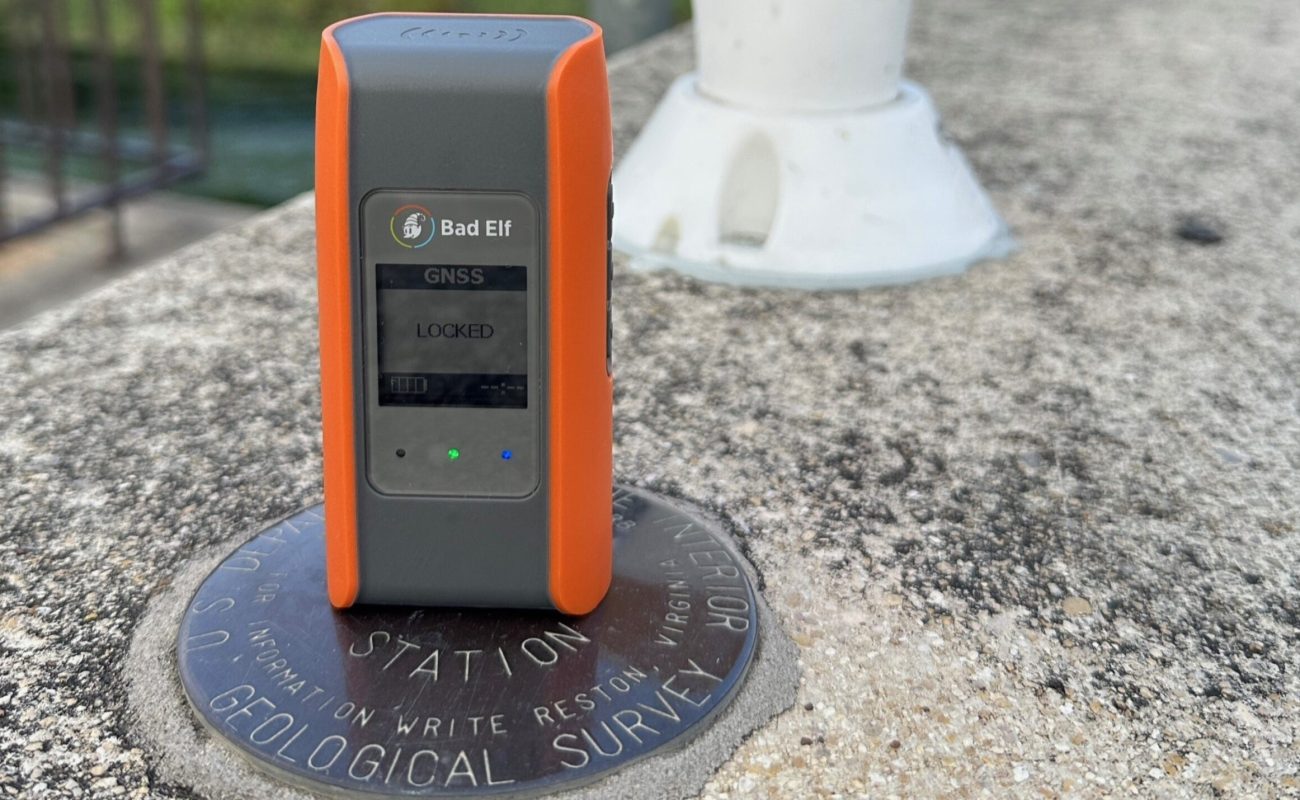
Inaccurate GPS data can lead to costly errors in utility surveying, construction, and asset monitoring. Fortunately, with the Bad Elf Flex Mini, you can turn your smartphone, tablet, or laptop into a high-precision tool capable of delivering centimeter-level accuracy using RTK corrections.
The Bad Elf Flex Mini is a powerful, low-cost GNSS receiver, ideal for anyone looking to efficiently capture high-accuracy location data in the field. Whether you’re a novice in geospatial technology or a seasoned professional, the Flex Mini’s rugged design, ease-of-use, and reliable results make it an essential tool for accurate field data collection.

As a mapping-grade GNSS receiver, the Flex Mini delivers reliable 1.5-2 meter accuracy to any location-aware app on Android, iOS, and Windows via Bluetooth or USB. That’s already more than twice the typical smartphone accuracy of 3-5 meters. By upgrading to the Flex Mini Extreme configuration, users unlock the power of Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) corrections and can enhance their accuracy down to the centimeter level.
This article will cover the key features of the Flex Mini Extreme and how to set it up with Skylark Nx RTK corrections, the Skylark variant that achieves centimeter-level accuracy. Skylark Nx RTK is a highly reliable cloud-based GNSS corrections service compatible with all RTK receivers with an NTRIP client. By using global atmospheric modeling to smooth ionospheric and tropospheric irregularities, Swift’s network RTK solution delivers improved accuracy at longer baselines (you can learn more about Skylark and its variants here).
Features
The Flex Mini Extreme supports RTK corrections from corrections service providers such as Swift Navigation, making it perfect for high-precision applications in sectors like construction or utilities, where professionals rely on RTK receivers to lay out plots or map pipelines but do not want to go through the hassle of setting up their own local base station. By supporting multiple GNSS constellations (GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS, Galileo, and QZSS) and multiple frequencies (L1 and L5), accuracy is improved even in challenging environments with signal obstructions such as inside urban canyons or under tree canopies.
Other key features include a 24-hour battery life, IP67 weatherproofing, and an operating temperature range of -20 to 55°C (-4 to 131°F) allowing for extended fieldwork in any weather on a single charge. Weighing just 143 grams (5 oz), the Flex Mini is lightweight and portable, making it convenient to carry in a pocket or glove compartment when on the go. The Flex Mini was also among the first devices of its kind to receive Apple’s Made for iPhone (MFi) certification, ensuring all running iOS apps automatically utilize its location data, without any additional configuration needed.
For the full list of technical specifications, visit Bad Elf’s Flex Mini product page.
Setting up the Bad Elf Flex Mini With Skylark RTK Corrections
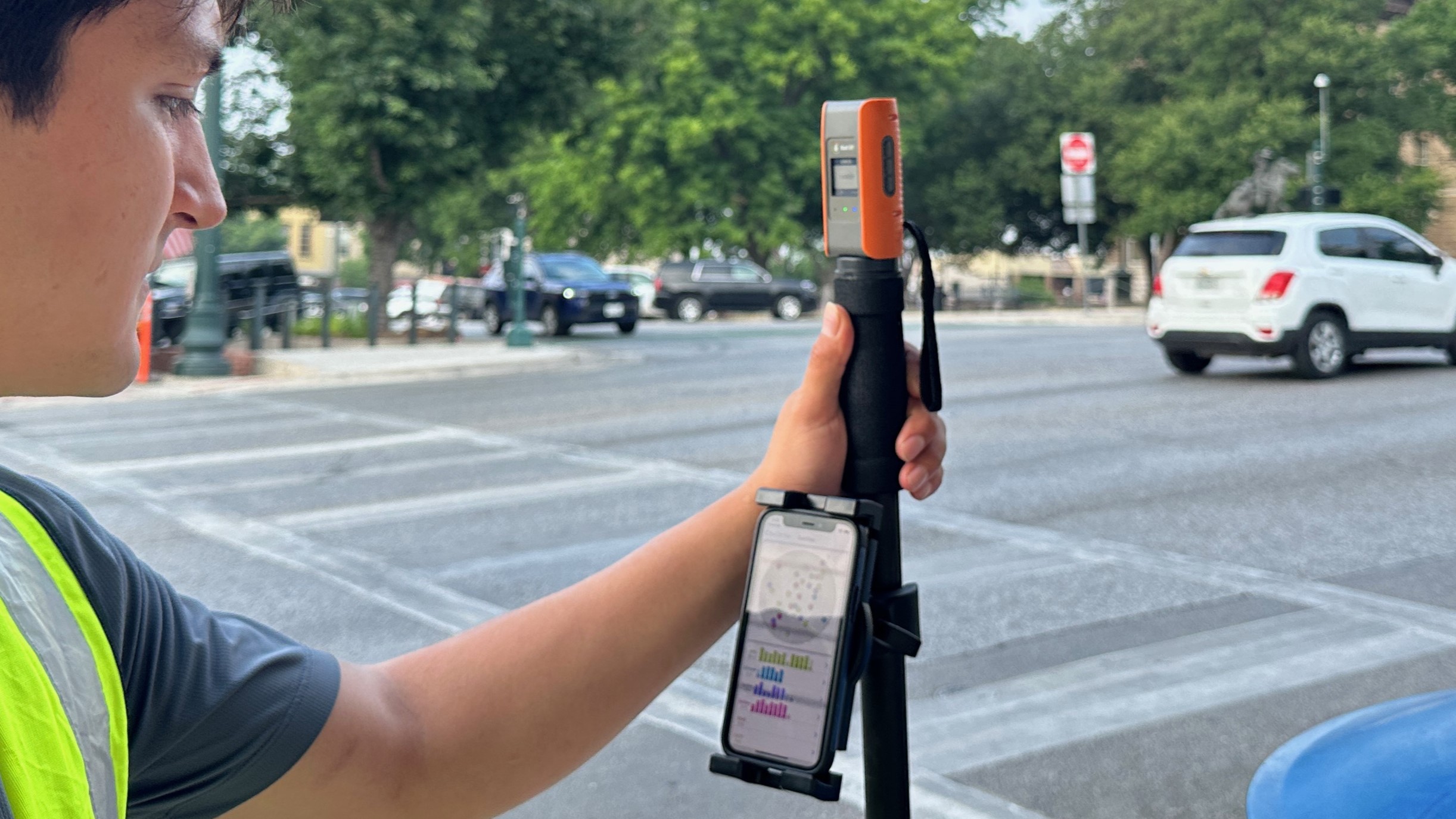
Setting up the Flex Mini with RTK corrections is quick and straightforward, allowing users to achieve highly accurate data collection with minimal hassle. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you unlock the full potential of your Flex Mini.
First, turn on your Flex Mini and pair it with your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth in the device’s settings (a blue light will confirm successful pairing).
Next, on your mobile device’s app store, locate and download the Bad Elf Flex app. The app will immediately recognize the paired receiver.
Now that the device is paired, you’ll need to configure the RTK settings to begin ingesting corrections. In the app, go to Correction Mode > RTK via NTRIP > Network, and tap the “+” sign to create a new profile.
Give the NTRIP profile a name, “Skylark Nx RTK” for example. Then head to Swift’s Skylark User Portal, sign up and subscribe to Skylark if you haven’t already.
The next field to fill out is the host. In the Skylark User Portal, make sure to select the one that corresponds to your region (NA for North America, EU for Europe, AP for Asia Pacific) and has L1+L5 as frequencies. Copy and paste the resulting address as the host, then the port, username, password, mount point – which in the case of Skylark Nx RTK – is “NXRTK-MSM5”, and finally, the datum which depends on your specific use case.
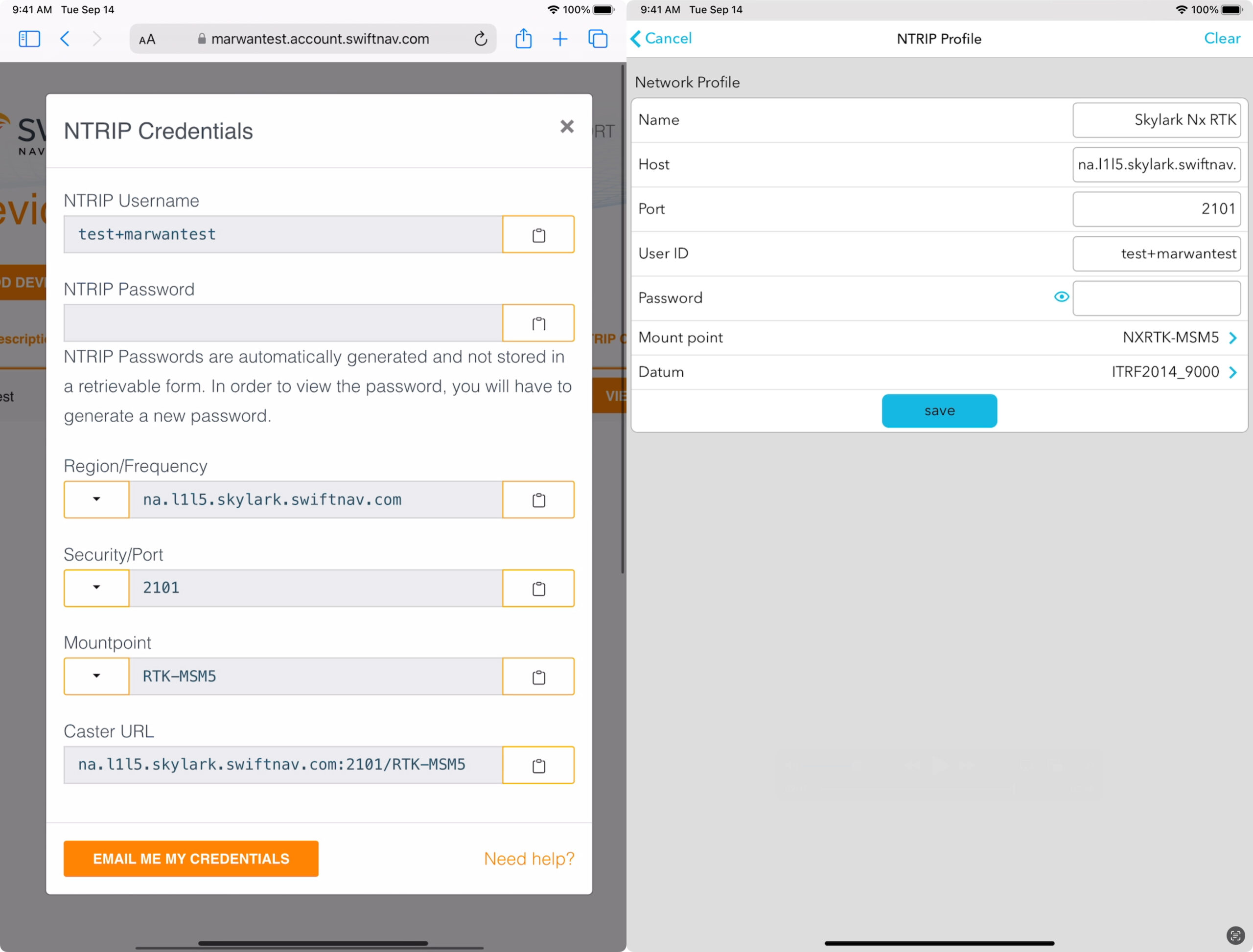
Save this configuration and tap Connect in the profile you just created. You’re now ingesting RTK corrections, it is that easy!
As mentioned earlier, all apps receive their location data from the connected receiver without any additional configuration needed. Additionally, the Flex Mini also offers direct integrations with a plethora of supported apps (such ArcGIS Field Maps or GIS Cloud MDC), allowing for more control and visibility over the receiver directly from the 3rd-party app (such as monitoring the RTK fix mode and reported accuracy). Some of these integrations even allow further customization, such as setting the pole height for ArcGIS Field Maps to accurately record vertical elevations, accessible via Data Collection > Flow Points to 3rd-Party App.
With the Flex Mini set up and ready, you’re now equipped for high-precision data collection in the field. For optimal RTK performance, ensure you have a stable internet connection. Regularly update the firmware of your Flex Mini to benefit from the latest improvements and bug fixes.
How are Network RTK corrections transformative for GIS?
There are two primary approaches to implementing RTK corrections for geographic data collection: Network RTK and RTK from a local base station.
Network RTK utilizes a web of multiple reference stations distributed over a wide area. This ensures consistent and reliable corrections across the coverage area, reducing the impact of localized errors. On the other hand, RTK from a local base station involves a single, locally placed reference station providing corrections to the rover (moving receiver). This provides highly accurate location data within a limited radius, however, these base stations are costly and the quality of corrections deteriorates with distance from the base station. A key advantage of Swift’s network RTK solution is its ability to cover a large geographic area at a lower cost, making it ideal for large-scale operations that require extensive coverage.
Learn more about Swift Navigation’s GIS Solution.
Contact Swift for help in improving your data collection process.
Read about our partnership with Bad Elf.