What is GNSS Accuracy?
Accuracy in positioning systems refers to how closely the estimated or measured position matches the true position of an object or vehicle. In GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) applications, accuracy is typically quantified as the statistical difference between the reported and actual positions, often expressed as a confidence interval (e.g., 95% of errors are less than a certain distance).
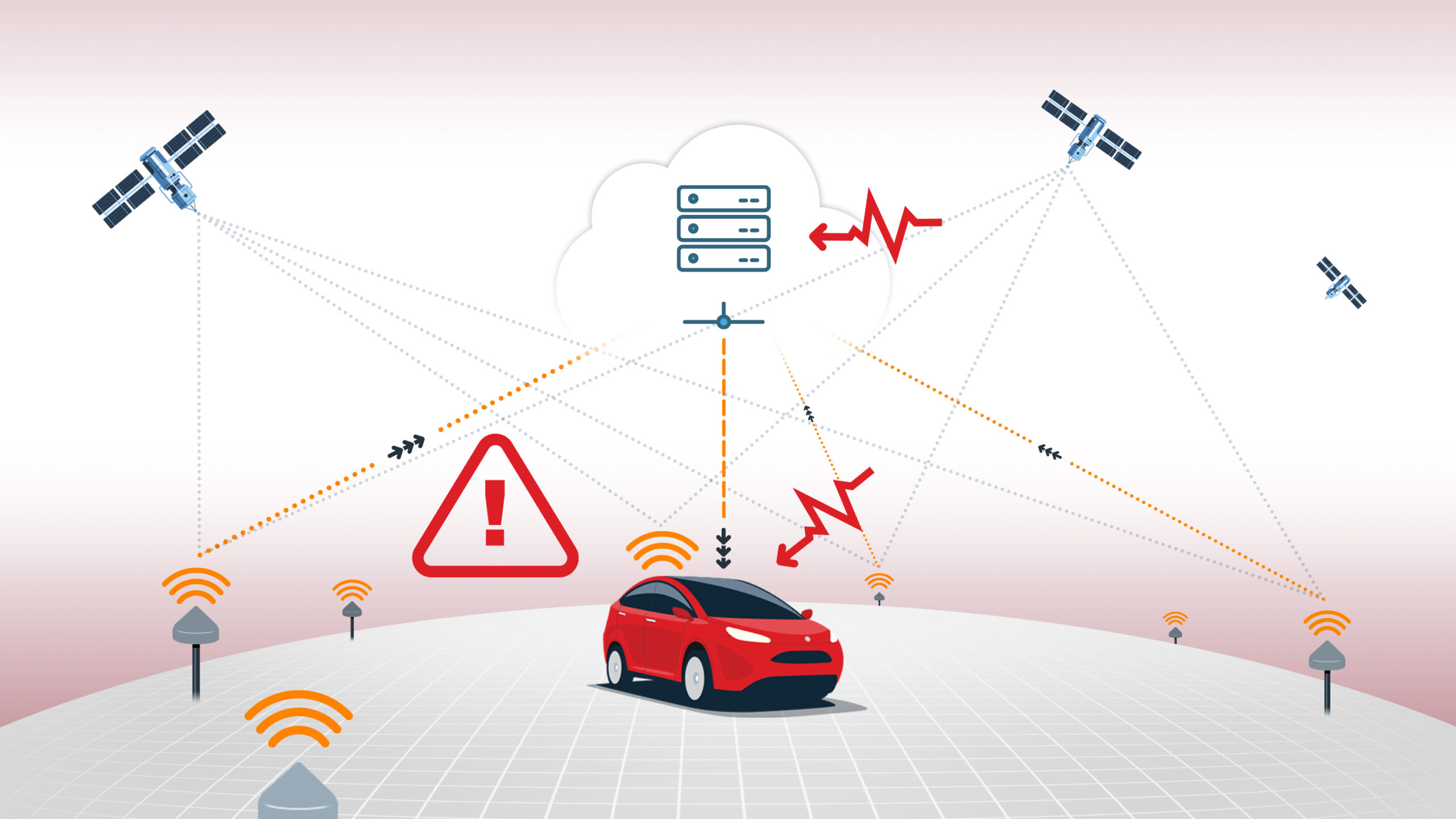
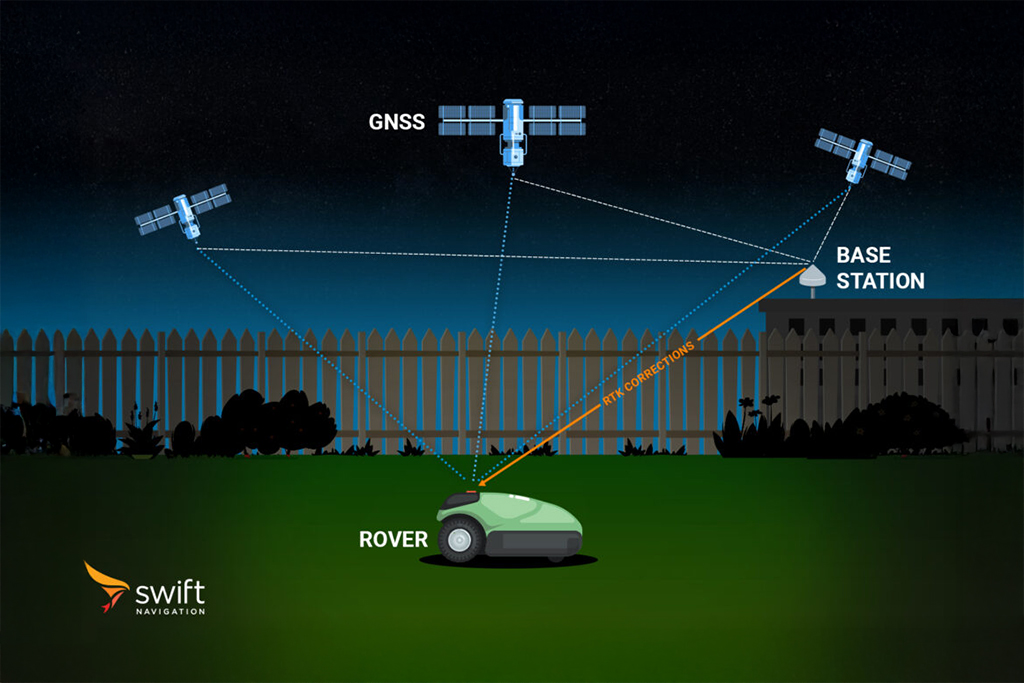
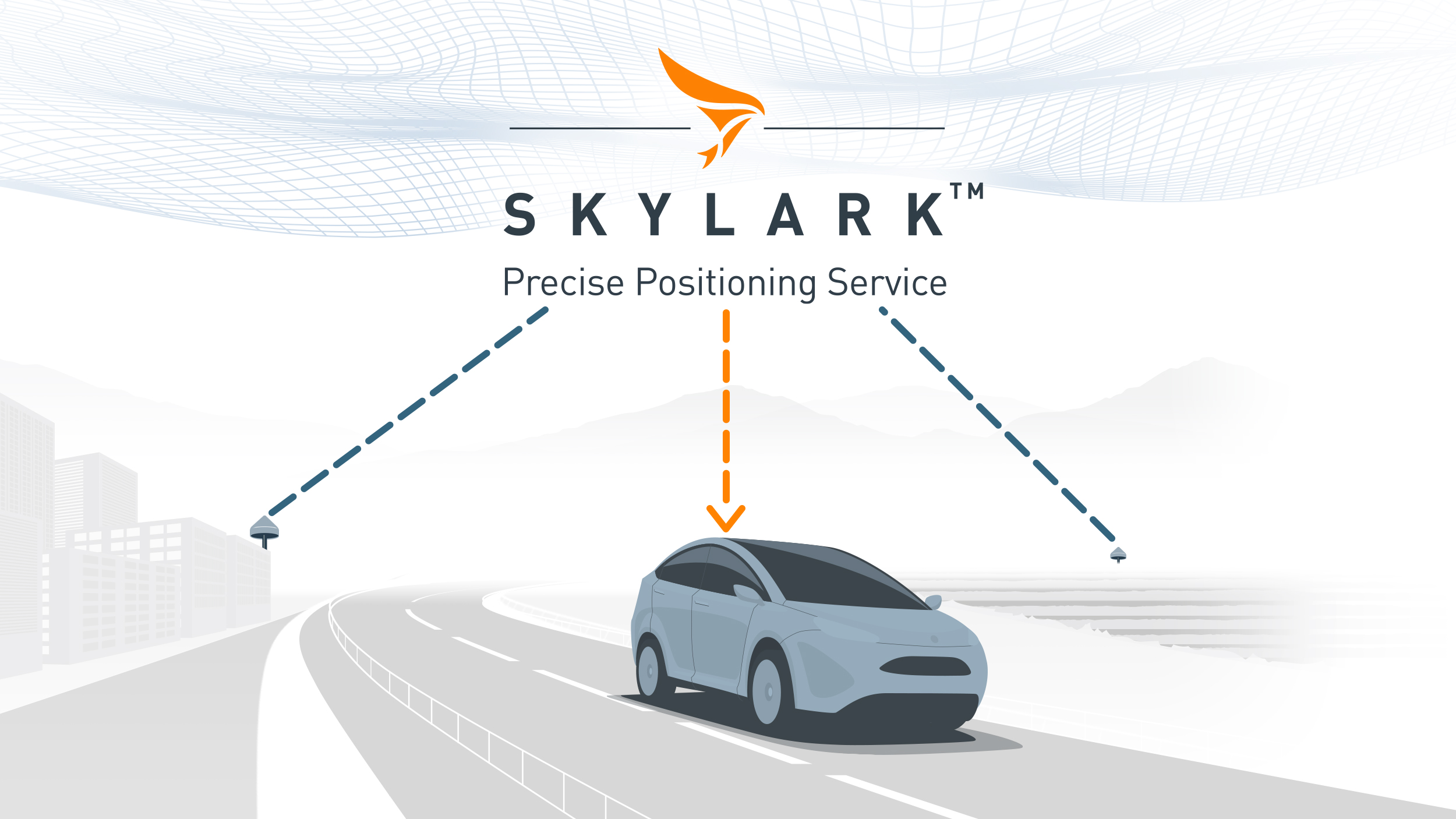
High accuracy is essential for applications like autonomous vehicles, ADAS, robotics, and fleet management, where lane-level or even sub-meter precision is required for safe and reliable operation. For example, cloud-based GNSS correction services such as Skylark can improve standard GPS accuracy from several meters down to just a few centimeters, enabling precise lane identification and robust navigation even in challenging environments like urban canyons or tunnels.
Accuracy is a foundational metric in evaluating the performance of any positioning solution, and it is closely monitored and validated through extensive testing across diverse environments to ensure reliability and safety for end users. While accuracy refers to closeness to the true position, it is often discussed alongside precision, which describes the consistency or repeatability of position measurements over time.
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp