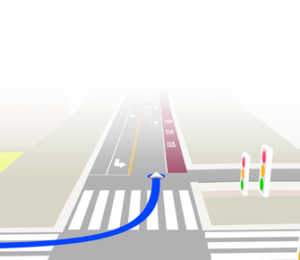
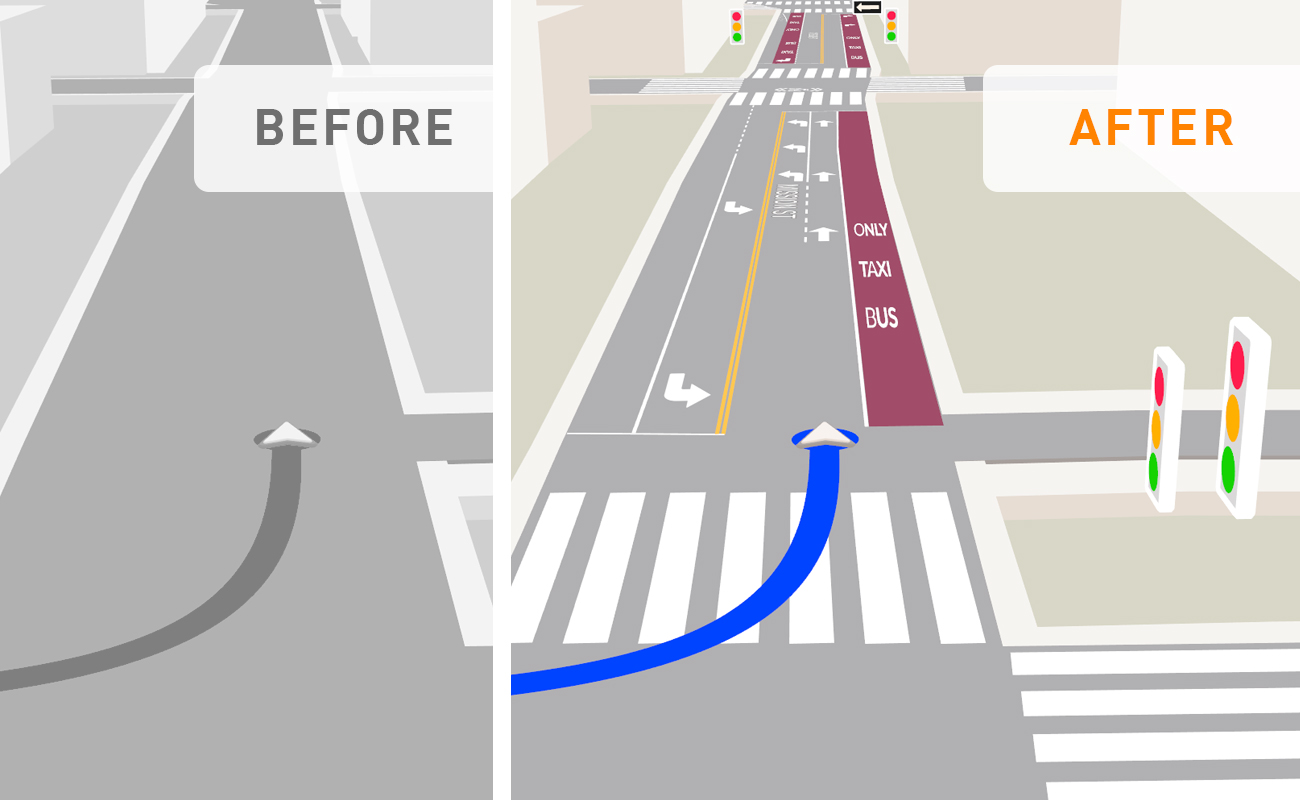
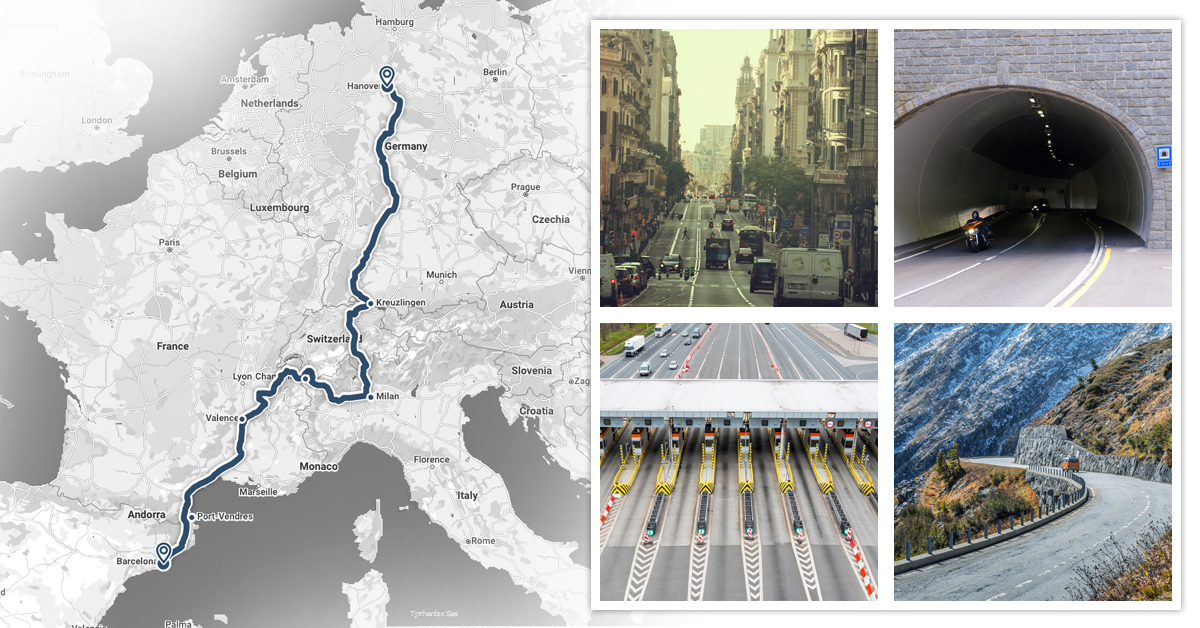
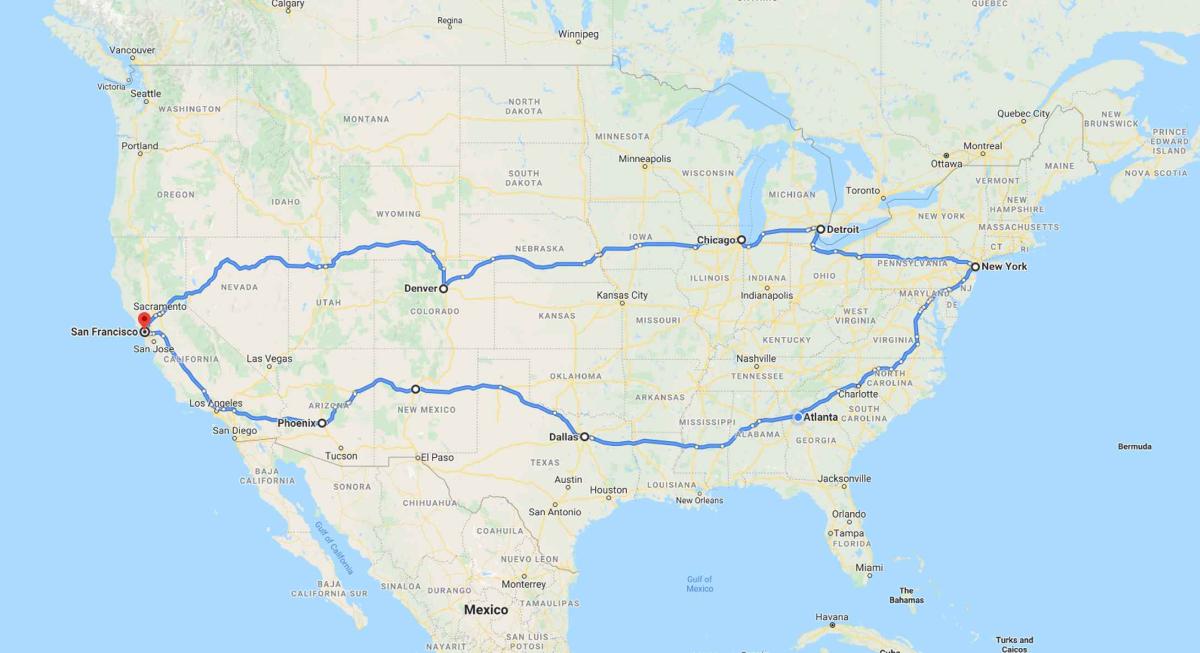
What is Dead Reckoning?
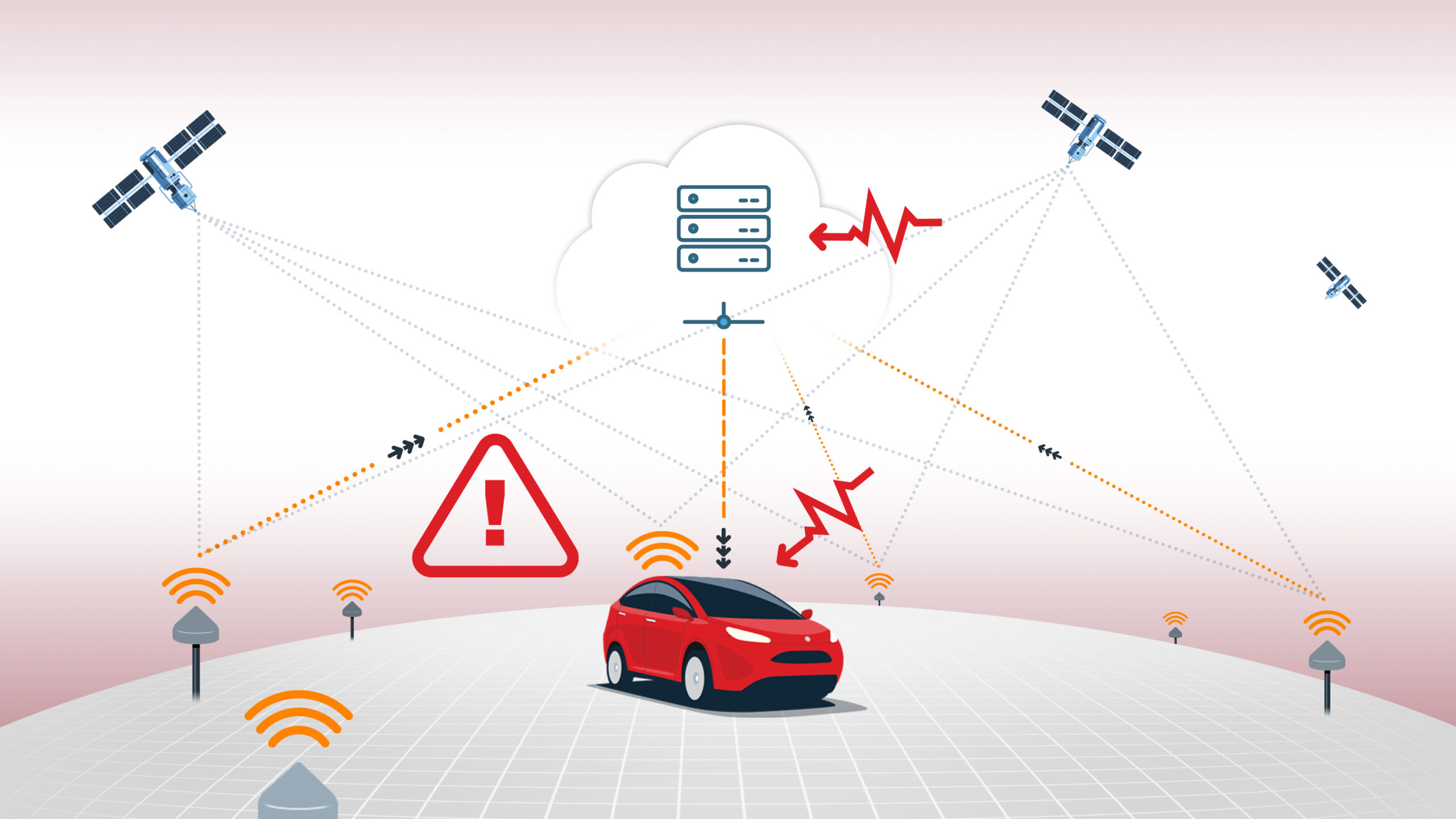
Dead reckoning is a navigation technique that estimates a vehicle or object’s current position based on a previously determined position, updated by measurements of speed, direction, and elapsed time. In modern navigation systems, dead reckoning complements GNSS positioning in environments where satellite signals are unreliable or unavailable, such as: tunnels, urban canyons, or dense forests.
Dead reckoning systems typically use inertial sensors (accelerometers and gyroscopes) and may also incorporate wheel odometry or other vehicle sensors to track movement. By integrating these sensor inputs, dead reckoning can maintain accurate position estimates during GNSS outages, though errors accumulate over time due to sensor drift and biases.
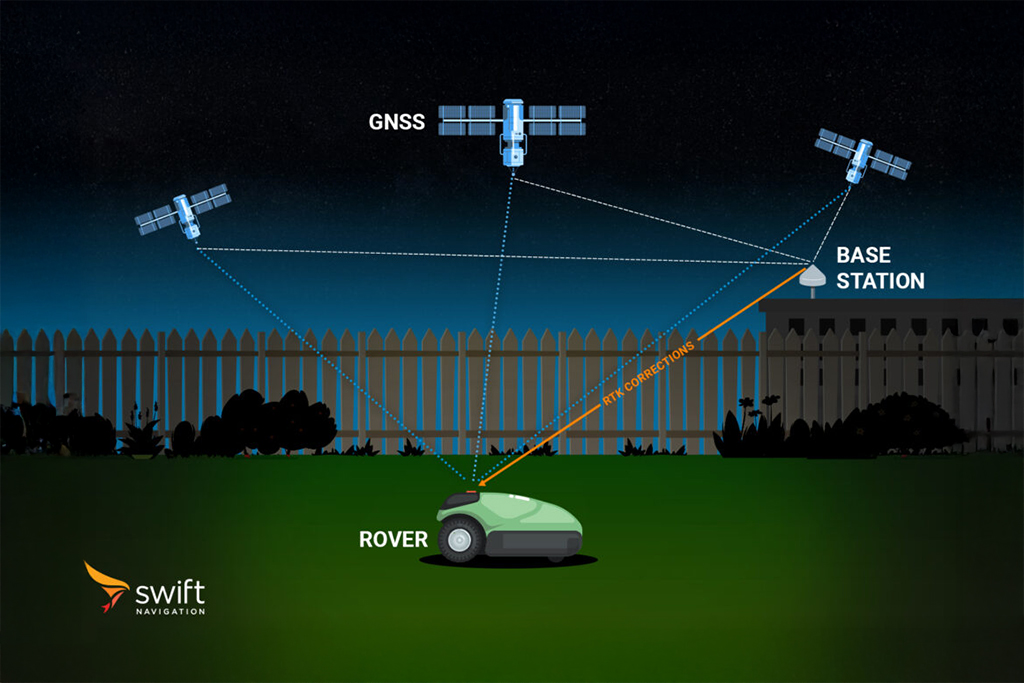
In automotive applications, dead reckoning is often fused with GNSS within a positioning engine to provide robust and continuous navigation. Swift Navigation’s Starling positioning engine, for example, uses loosely coupled sensor fusion to combine GNSS, inertial data, and vehicle dynamics for consistent accuracy even in challenging conditions.
Related Content
Automotive

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Joel Gibson

Marwan Ramadan

Anthony Cole

Anthony Cole

Marwan Ramadan

James Tidd
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp