What is a GNSS Constellation?
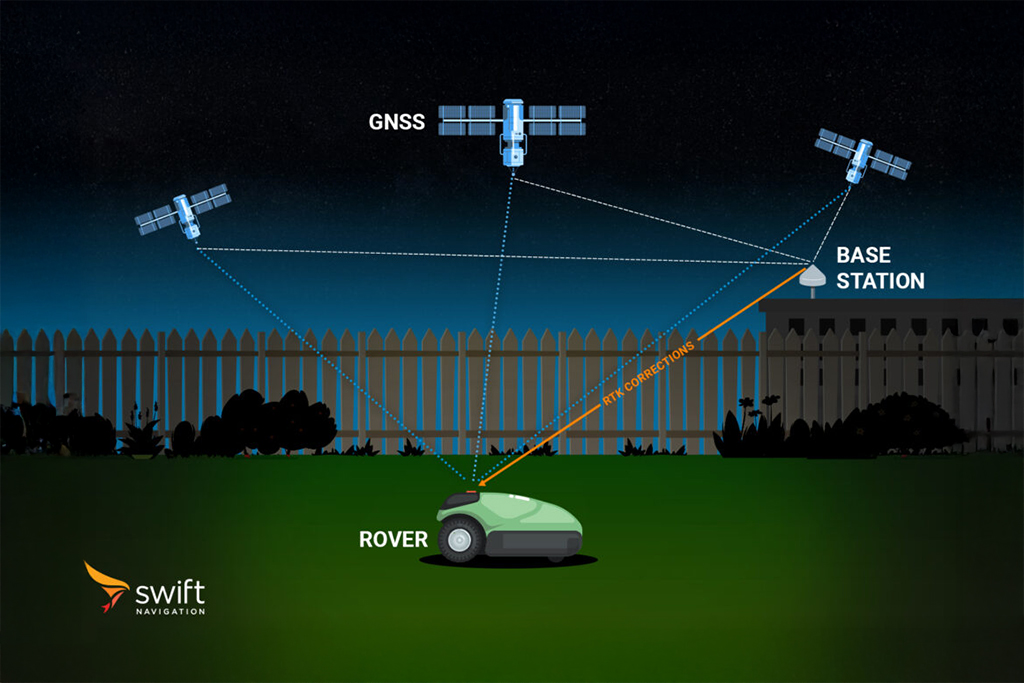
In satellite navigation, a constellation refers to a group of satellites working together to provide global or regional positioning services. Each global navigation satellite system operates its own constellation, GPS for example. The arrangement and number of satellites in a constellation are designed to ensure that users on Earth can receive signals from multiple satellites at any time, enabling accurate position calculations.

Multi-constellation GNSS receivers can use signals from several systems simultaneously, increasing the number of visible satellites and improving positioning accuracy, reliability, and availability. This is especially important in urban canyons or areas with obstructed views of the sky. The main GNSS constellations are GPS (United States), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), BeiDou (China), and QZSS (Japan).
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp