Back to Blog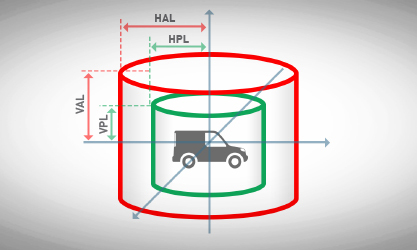
White Paper
Integrity Concept for the Safe Operation of the Swift Navigation Positioning System

This white paper outlines the integrity concept and parameters employed by Swift Navigation’s automotive positioning solution. The purpose of the integrity concept is to define a set of metrics and criteria from which safe operating conditions can be derived.
GNSS positions are defined in terms of the following parameters.
- Accuracy: GNSS position error (PE) is the difference between the estimated position and the actual position.
- Availability: The availability of a positioning system is defined as the ability to provide the required function and performance during the intended operation. The availability is characterized by the portion of time the system is to be used for navigation during which reliable position information is presented to integrated system.
- Continuity: The continuity of a system is the ability of the total system to perform its function without unscheduled interruption during the intended operation. More specifically, continuity is the probability that the specified system performance will be maintained for the duration of a phase operation, presuming that the system was available at the beginning of that phase operation and was predicted to operate throughout the operation.
- Integrity: Integrity is a measure of the trust that can be placed in the correctness of the information supplied by the positioning engine. Integrity includes the ability of a system to provide timely and valid warnings to the user (Alerts) when the system must not be used for the intended operation. Integrity requirements are defined with four parameters:
- Integrity risk (P -int ): The integrity risk is the probability (per unit of time) of providing a position that is out of tolerance without warning the user within the time-to-alert.
- Alert limit (AL): To ensure that the position error is acceptable, an alert limit is defined. It represents the largest position error allowable for a safe operation. The position error cannot exceed this alert limit without annunciation.
- The Horizontal Alert Limit (HAL) is the radius of a circle in the horizontal plane, with its center being at the true position, that describes the region that is required to contain the indicated horizontal position with the required probability for a particular navigation mode.
- The Vertical Alert Limit (VAL) is half the length of a segment on the vertical axis, with its center being at the true position, that describes the region that is required to contain the indicated vertical position with the required probability for a particular navigation mode.
- Time to Alert (TTA): The TTA is the maximum allowable elapsed time from the onset of a positioning failure (position out of tolerance) until an alert is annunciated.
Read the full white paper to learn more about automotive safety requirements and establishing safe operations for a positioning system.
