What is GNSS?
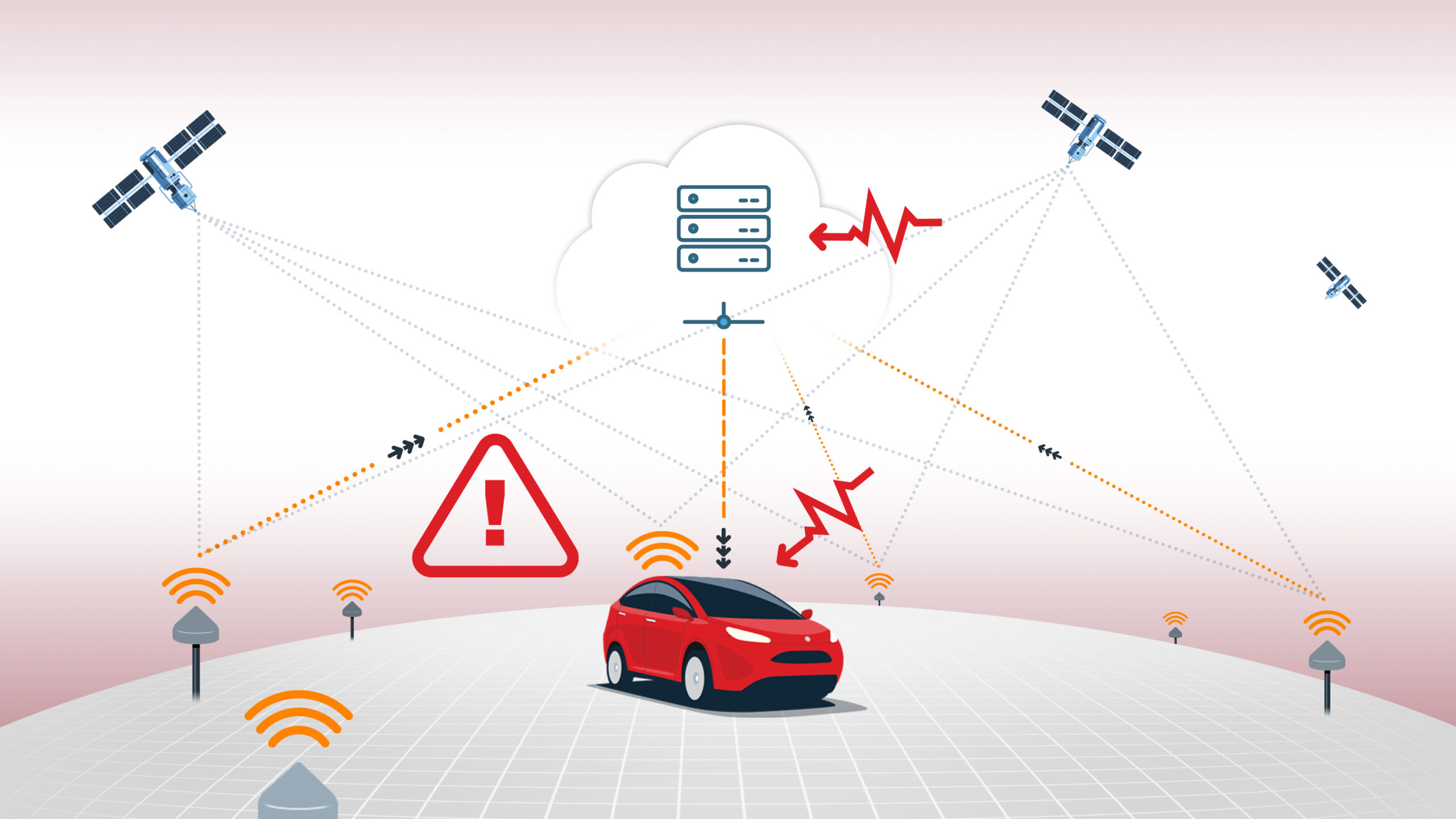
GNSS stands for Global Navigation Satellite System, an umbrella term for any satellite constellation that provides global positioning, navigation, and timing services. The primary GNSS constellations are GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), and BeiDou (China), with regional systems like QZSS (Japan) and NavIC (India) supplementing coverage. GNSS receivers use signals from multiple satellites across these constellations to calculate precise positions on or near the Earth’s surface. By leveraging multiple constellations and frequencies, modern GNSS solutions achieve higher accuracy, faster convergence times, and greater robustness against signal blockages or interference.
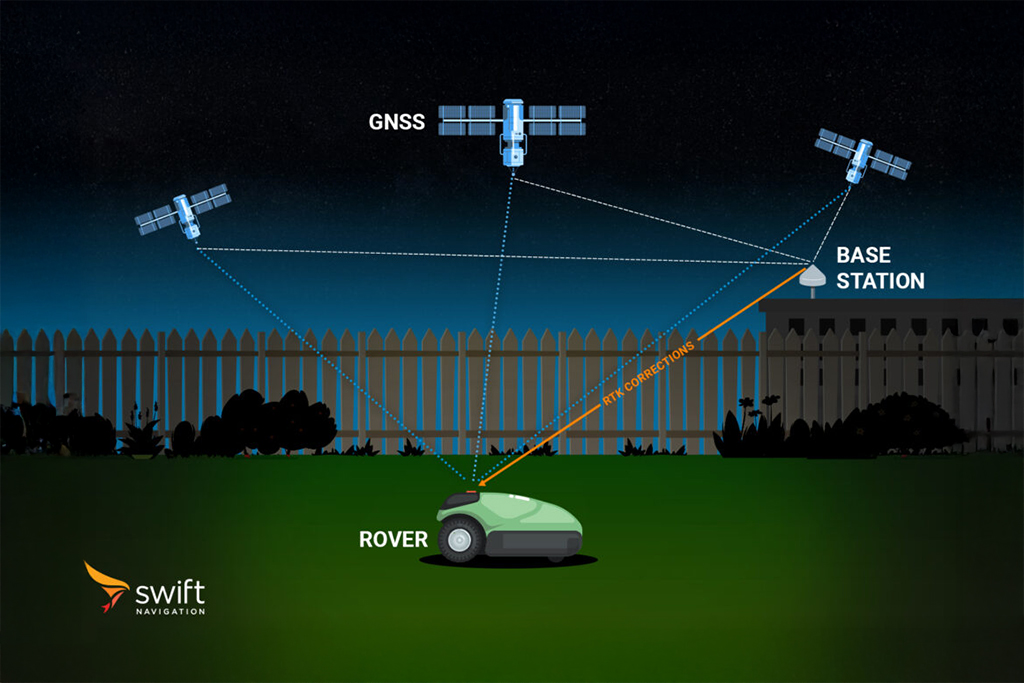
GNSS technology underpins a vast range of applications, from autonomous vehicles and ADAS to surveying, agriculture, logistics, and mobile devices. GNSS correction services such as RTK and PPP further enhance GNSS accuracy to centimeter levels for precision-critical use cases.
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp