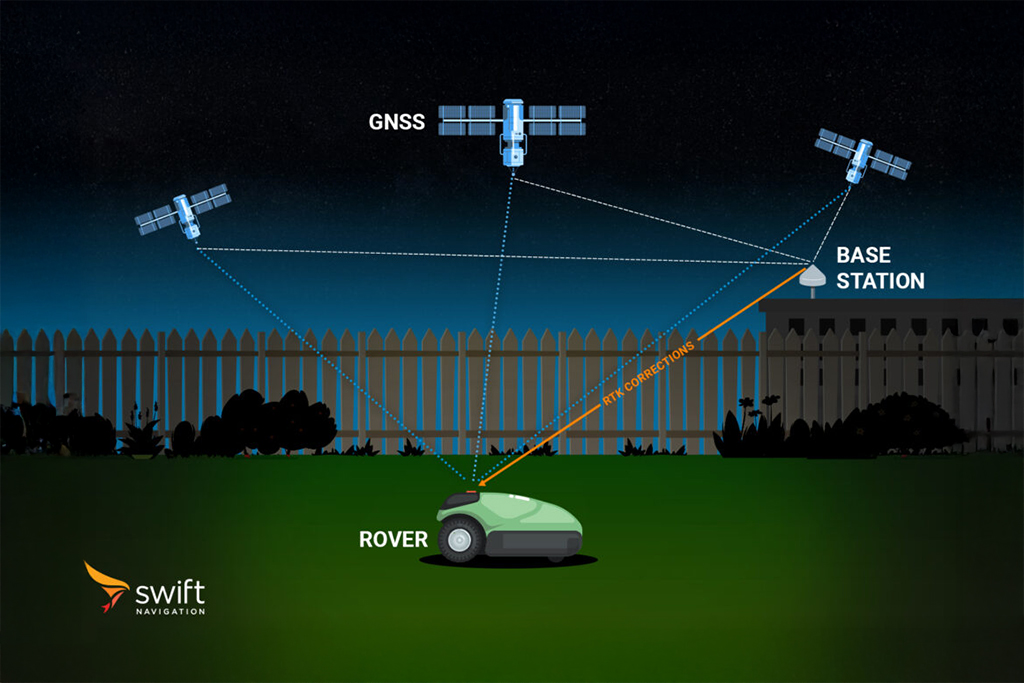
What Are GNSS Observations?
In GNSS terminology, “observations” refer to the raw measurements made by a GNSS receiver from satellite signals. These include measurements of:
- Pseudorange: The measured distance between the receiver and each satellite, based on signal travel time.
- Carrier Phase: The phase of the carrier wave received from each satellite, used for high-precision positioning.
- Doppler Shift: The change in frequency of the received signal due to relative motion between satellite and receiver.
Observations are fundamental to all GNSS positioning techniques. They form the core data used to compute position solutions, whether for standard navigation or advanced methods like RTK. In RTK and networked correction systems, observations from reference stations are used to generate correction data that can be applied by rovers to achieve centimeter-level accuracy.
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp
Product Marketing Manager
October 22, 2025

Marwan Ramadan
Senior Director, Product Marketing
October 10, 2025

Marwan Ramadan
Senior Director, Product Marketing
June 11, 2025

Devon Sharp
Product Marketing Manager
May 2, 2025

Devon Sharp
Product Marketing Manager
February 10, 2025

Marwan Ramadan
Senior Director, Product Marketing
January 28, 2025

Devon Sharp
Product Marketing Manager
January 15, 2025

Marwan Ramadan
Senior Director, Product Marketing
November 12, 2024
GIS

Devon Sharp
Product Marketing Specialist
October 10, 2024

Devon Sharp
Product Marketing Manager
June 26, 2024
ROBOTICS

Marwan Ramadan
Senior Director, Product Marketing
November 18, 2025

Rai Gohalwar
Staff Systems Test Engineer
April 4, 2024