What is Differential GNSS (DGNSS)?
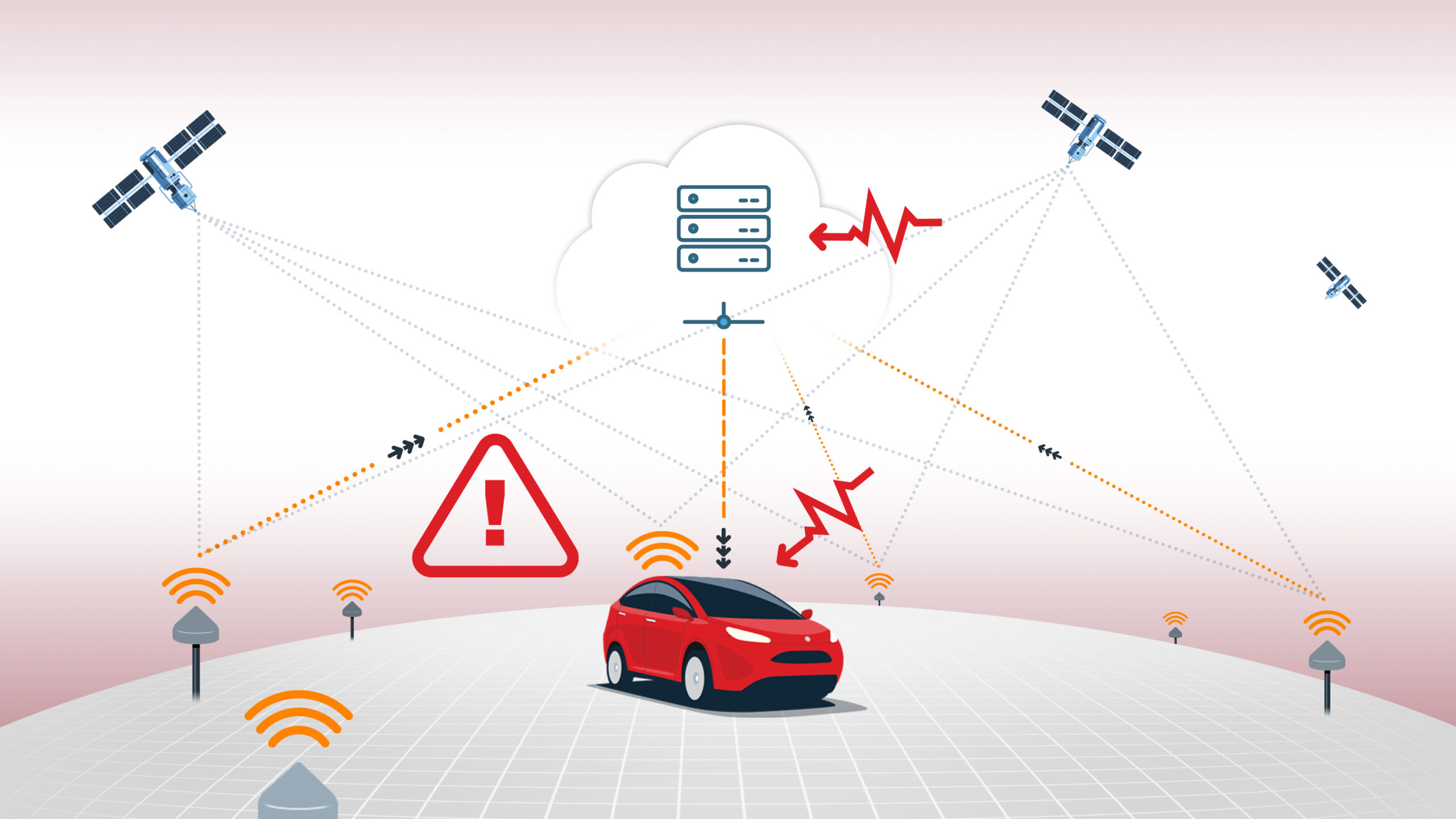
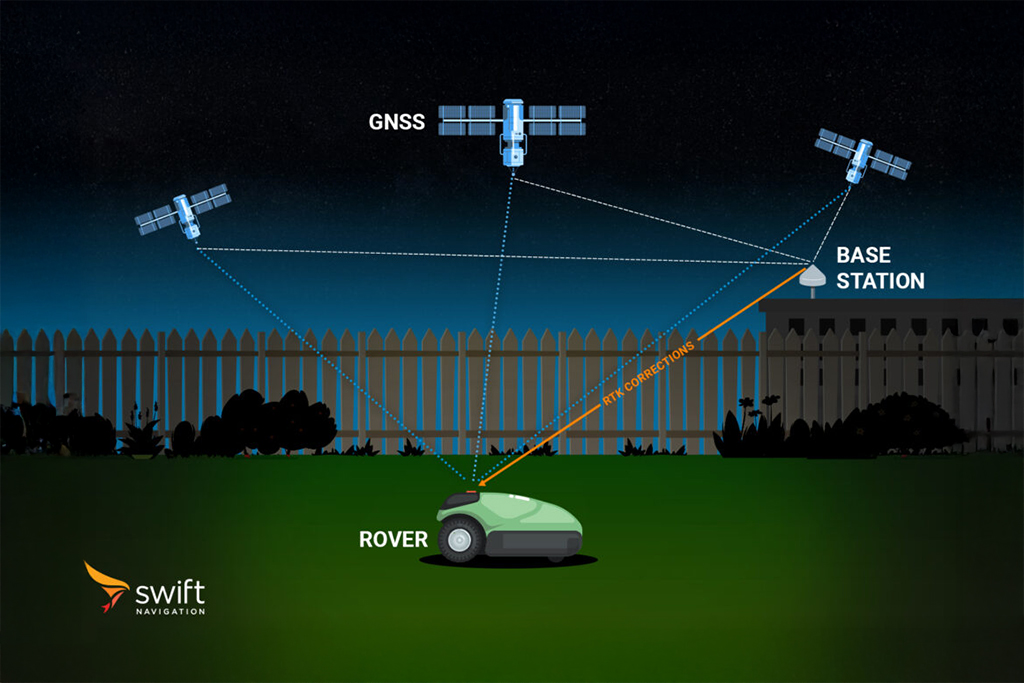
Differential GNSS (DGNSS) is a technique that enhances the accuracy of standard GNSS positioning by using correction data from a base station at a known location. The base station receives satellite signals and compares its calculated position to its known position, determining the errors in the satellite signals. These corrections are then transmitted to nearby GNSS receivers (rovers), which apply them to their own measurements to improve positional accuracy. DGNSS corrections are typically applied at the code phase level, resulting in improved accuracy over standalone GNSS but generally less precise than carrier-phase-based methods like RTK (Real-Time Kinematic).
DGNSS is widely used in applications where sub-meter accuracy is sufficient, such as marine navigation, agriculture, and some surveying tasks. The main advantage of DGNSS is its ability to provide improved accuracy over larger areas compared to single-point GNSS solutions such as single-baseline RTK.
Swift Navigation offers Skylark™ Dx, a global DGNSS service designed to deliver uniform, continent-wide performance for demanding applications. Optimized for small, battery-powered devices, Skylark Dx features exceptionally low data and power consumption. Its ability to operate effectively at any signal-to-noise ratio makes it ideal for devices with constrained antennas, making it a great solution for mobile and asset tracking use cases.
For a more in-depth overview of Differential GNSS and how it compares to the other GNSS correction methods such as RTK, PPP-RTK and SBAS, read our blog What are the Different GNSS Correction Methods?
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan
GIS

Devon Sharp