What is Precise Point Positioning (PPP)?
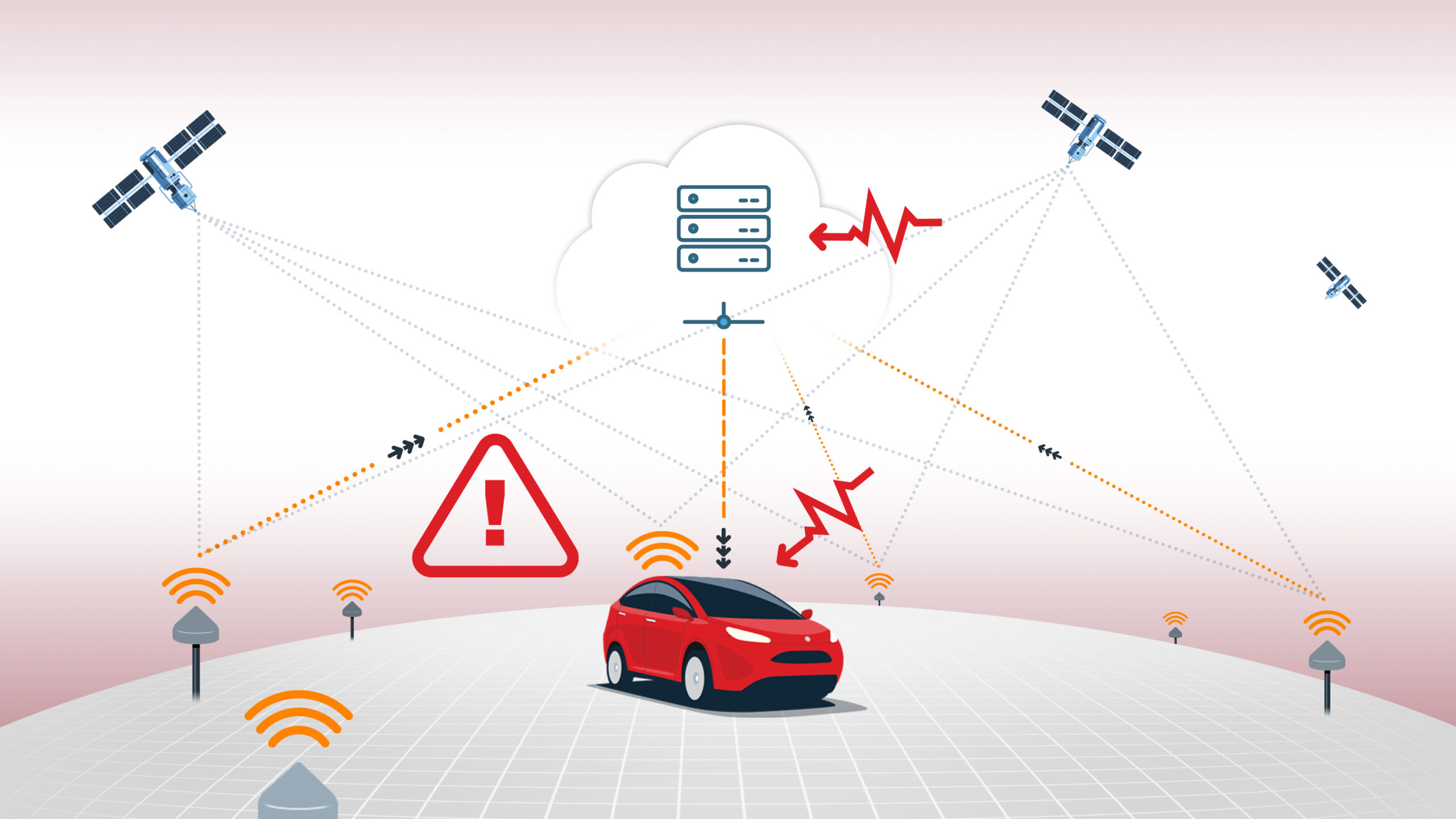
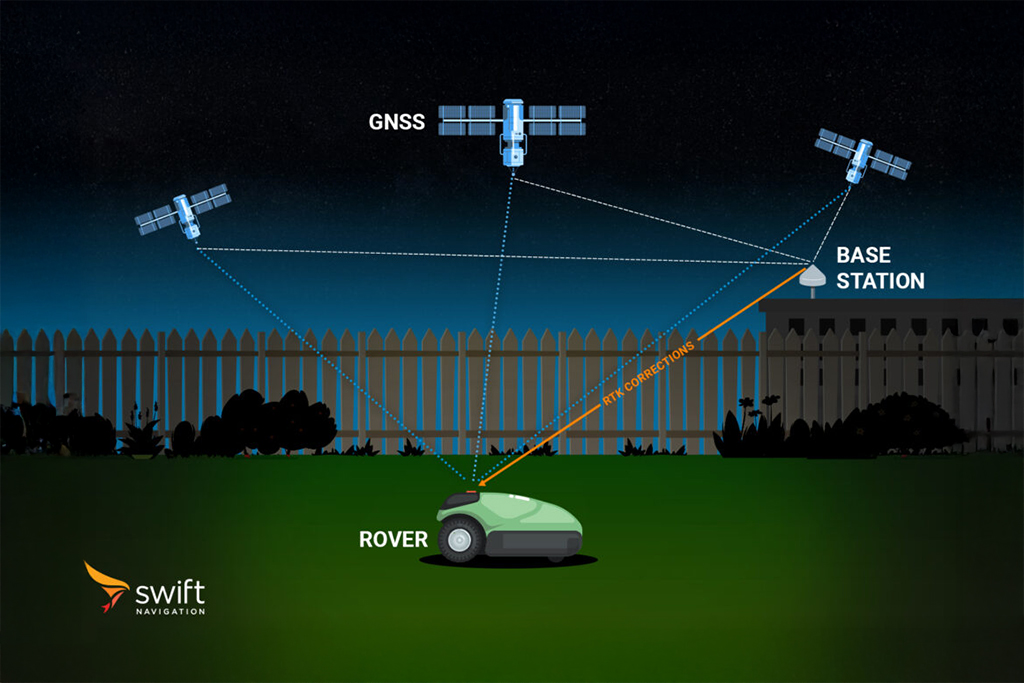
Precise Point Positioning (PPP) is an advanced GNSS correction technique that enables centimeter- to decimeter-level positioning accuracy globally, without requiring a local base station. Precise Point Positioning works by applying precise corrections for satellite orbits, clocks, and atmospheric delays, derived from a global network of reference stations, to raw GNSS measurements at the user’s receiver. Unlike RTK (Real-Time Kinematic), which relies on nearby base stations for corrections, PPP users receive correction data via satellite or internet from centralized services.
Precise Point Positioning combines code-phase and carrier-phase measurements with sophisticated error modeling and ambiguity resolution algorithms. While Precise Point Positioning offers global coverage and high accuracy, it typically requires longer convergence times (several minutes to half an hour) as the receiver resolves carrier-phase ambiguities independently. Precise Point Positioning is widely used in surveying, autonomous vehicles, robotics, and any application requiring high-precision absolute positioning over large areas.
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan
GIS

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp
ROBOTICS

Marwan Ramadan