What is SBAS?
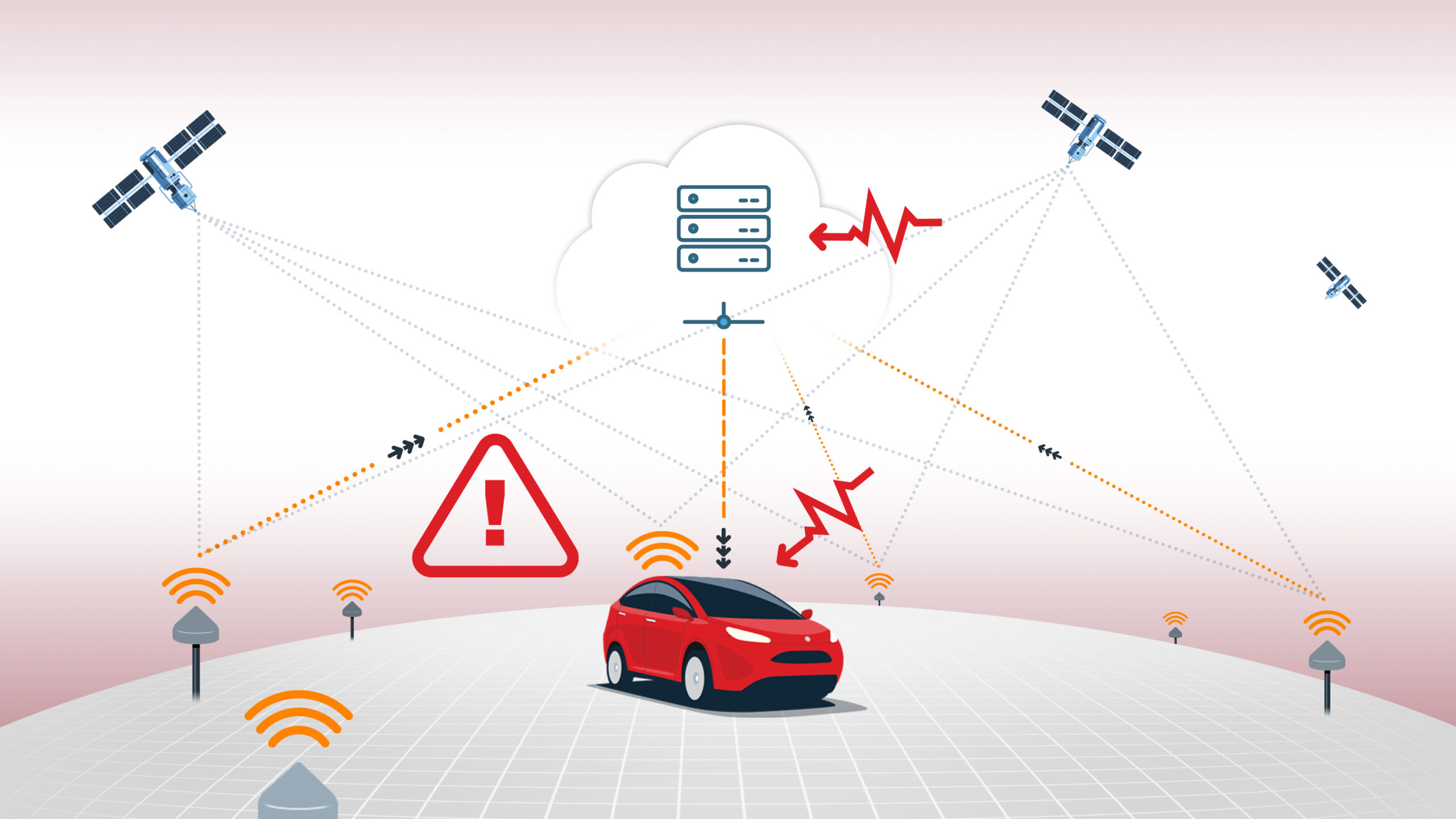
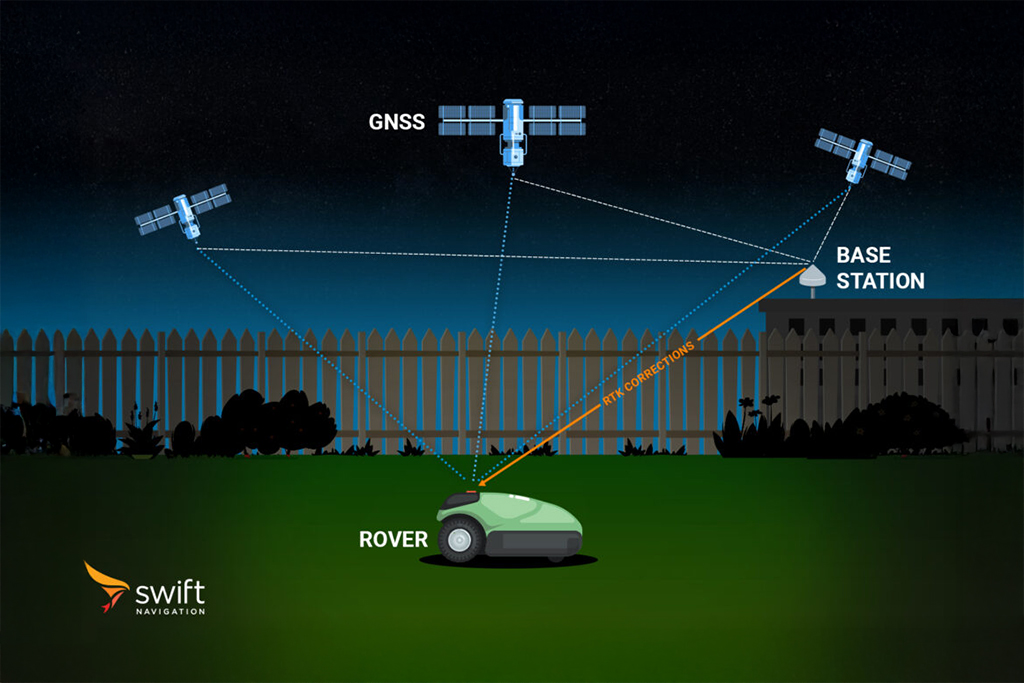
SBAS stands for Satellite-Based Augmentation System, a regional augmentation technology designed to improve the accuracy, integrity, and reliability of GNSS signals. SBAS operates by using a network of ground-based reference stations that monitor GNSS satellite signals for errors. These stations send their data to a central processing facility, which computes corrections for satellite orbit and clock errors as well as integrity information. The corrections are then broadcast to users via geostationary satellites covering large geographic regions.
SBAS is primarily used in aviation to support safe navigation and precision approaches, but it is also available for general use in many GNSS receivers. Examples include WAAS (USA), EGNOS (Europe), MSAS (Japan), and KASS (Korea). SBAS typically provides position accuracy within 1–3 meters, much better than uncorrected GNSS but not sufficient for applications requiring lane-level or centimeter accuracy. SBAS corrections are freely available and widely supported, making them a common baseline for comparison in positioning performance.
To learn more about SBAS and the other GNSS correction types, such as RTK and PPP-RTK, read our blog What are the Different GNSS Correction Methods?
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan
GIS

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp
ROBOTICS

Marwan Ramadan