What is a GNSS Rover?
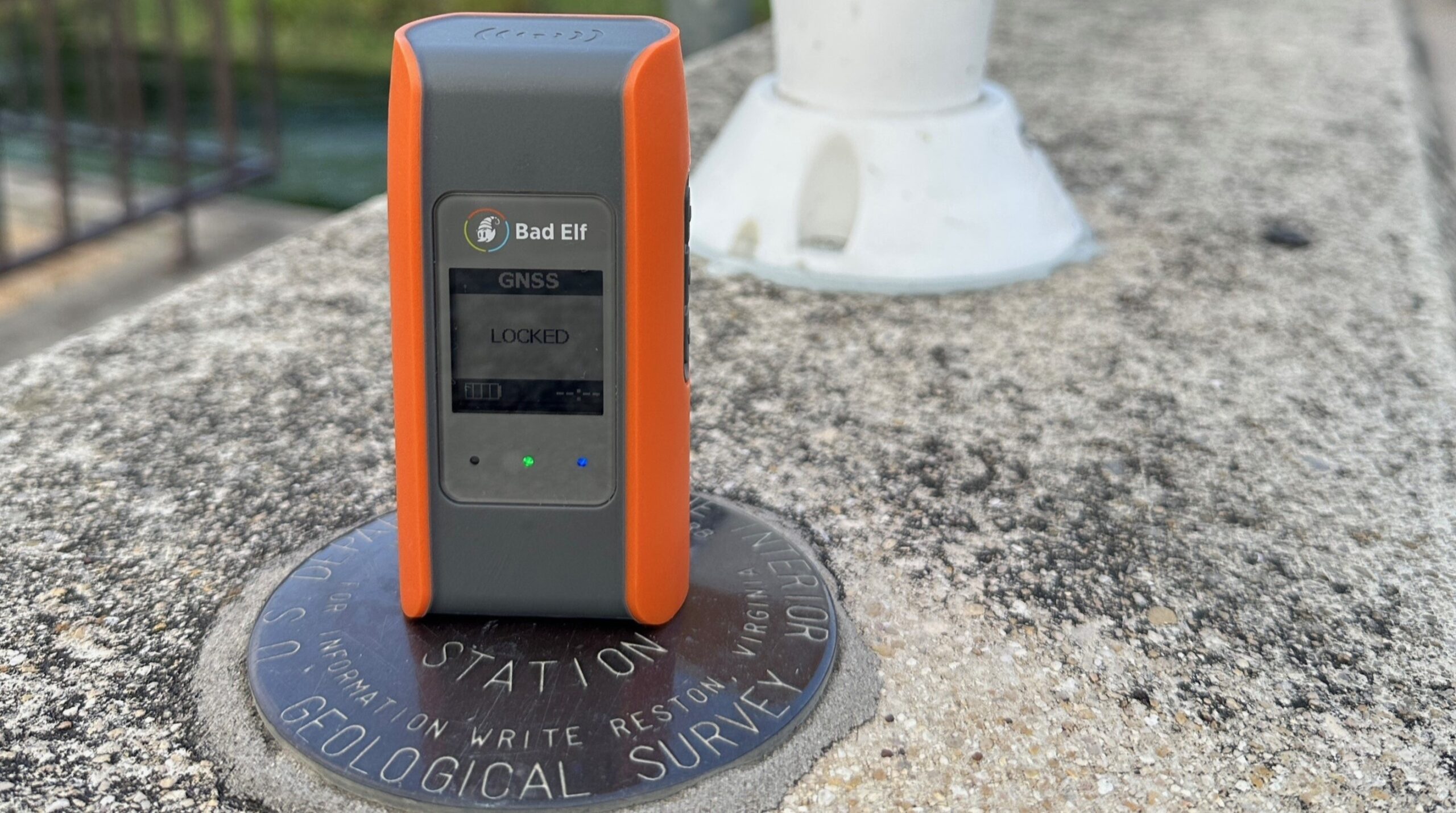
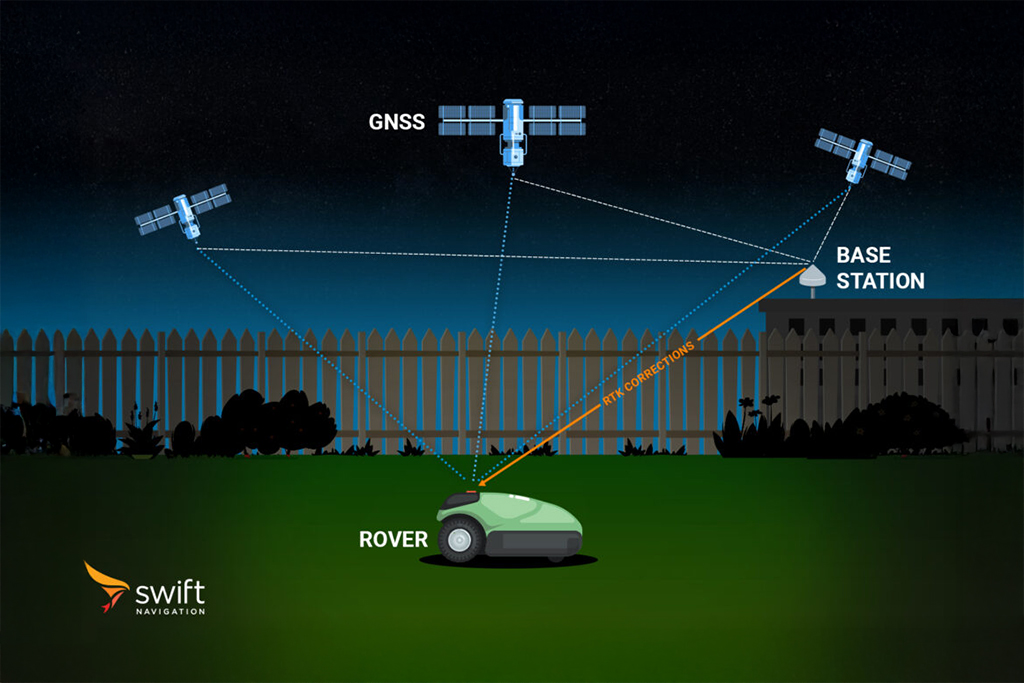
In GNSS terminology, a “rover” refers to the mobile component of a positioning system that determines its location relative to one or more reference stations (often called “base stations”). The rover can be any device equipped with a GNSS receiver, such as a vehicle, drone, robot, or handheld unit, whose position needs to be determined with high accuracy.
The rover receives satellite signals directly and may also receive correction data from a base station or a network of reference stations. These corrections are typically transmitted in real time using protocols like RTCM via NTRIP or other communication methods. By applying these corrections, the rover can achieve centimeter-level positioning accuracy using techniques such as Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) or Precise Point Positioning (PPP).
Rovers are central to applications requiring precise navigation and positioning, including surveying, autonomous vehicles, agriculture, robotics, and geospatial data collection. In post-processing workflows, rover observation data is often logged in RINEX format for later analysis or integration with base station data.
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan
GIS

Devon Sharp