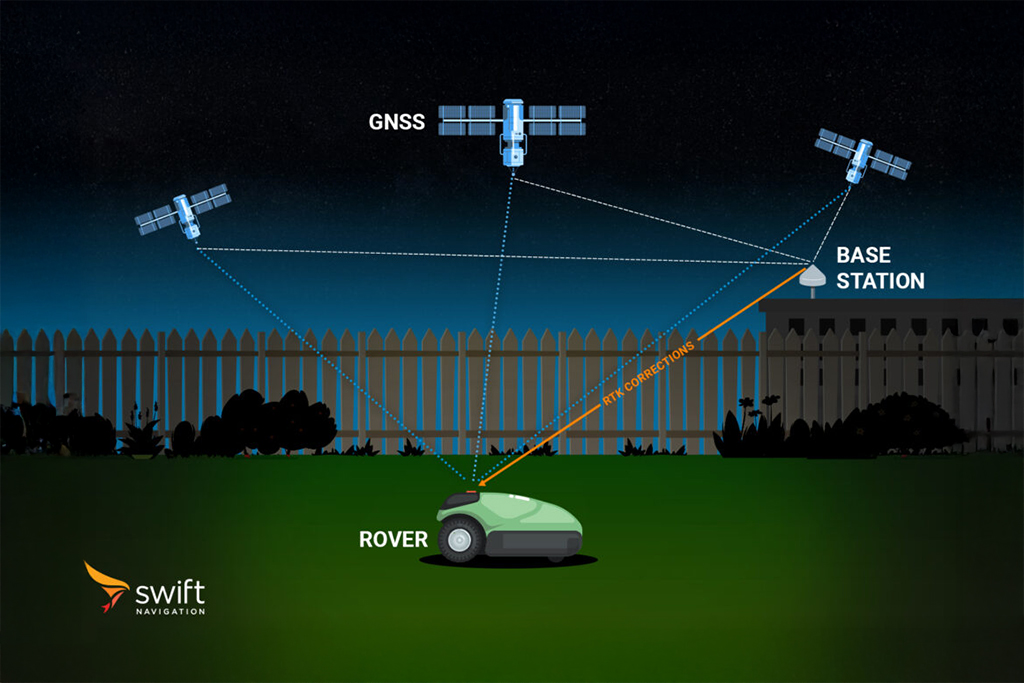
What is L Band?
L-band frequencies are a range of radio frequencies between 1-2 GHz used by GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) to transmit signals from satellites to receivers. These frequencies are integral to providing the high accuracy and reliability required for modern navigation applications, as combining signals from different frequencies allows GNSS receivers to minimize errors caused by atmospheric distortions and deliver enhanced positioning performance.
Spectrum Architecture
The L-band comprises two main sections:
- The Lower Band: 1164 MHz to 1300 MHz
- The Upper Band: 1559 MHz to 1610 MHz
Most satellite constellations transmit their data within these specific frequency ranges to ensure global compatibility.
Key L Band Frequency Designations
Within the L-band spectrum, there are several specific frequency designations commonly used in GNSS applications:
L1 Frequency: Operating around 1575 MHz, this is the primary GPS frequency that has been in use since the system’s inception. L1 carries the C/A (Coarse/Acquisition) code for civilian use.
L2 Frequency: Operating around 1227 MHz, L2 was originally designed for military use but now also carries civilian signals. The L2 band operates in unprotected spectrum and is susceptible to interference from civilian and military radars, aviation beacons, surveillance radars, mobile satellite services, and amateur radio broadcasting.
L5 Frequency: Operating around 1176 MHz, L5 is a newer frequency designed for modernized GNSS systems. L5 operates in a protected aviation band, reducing vulnerability to interference and ensuring more consistent performance compared to L2. The higher power and wider bandwidth of L5 signals reduce errors caused by multipath interference, making it particularly valuable for applications in complex environments like urban areas.
Different GNSS constellations utilize these L-band frequencies with their own designations. For example, BeiDou uses B1I and B1C (both around L1 frequency) and B2A (around L5 frequency). Galileo uses E1 (L1), E5a and E5b (L5 band components).
The Industry Shift: L1/L2 vs. L1/L5
The trend in the GNSS industry is moving toward L1/L5 dual-frequency configurations rather than the traditional L1/L2 combinations, as L5 adoption is gaining momentum with leading GNSS chipset manufacturers prioritizing L1/L5 configurations in their newest designs. This shift is driven by L5’s superior performance characteristics, better interference resistance, and future-proofing advantages as GPS modernization continues.
Read our article to learn more about L1/L2 vs L1/L5: Evaluating Dual-Frequency GNSS for High Precision Applications.
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan
GIS

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp
Robotics

Marwan Ramadan

Emily Pierce

Rai Gohalwar
Automotive

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Joel Gibson

Marwan Ramadan