What is a Reference Frame?
A reference frame (or geodetic datum) is a standardized coordinate system used to define precise locations on Earth. It provides the mathematical model for the Earth’s shape, size, orientation, and gravity field, enabling consistent and repeatable positioning across different regions and times. Reference frames are realized through networks of surveyed points whose coordinates are published relative to the frame’s definition.
There are two main types:
- Global Reference Frames: Such as ITRF2020 (International Terrestrial Reference Frame), WGS84 (used by GPS), which account for Earth’s dynamics including tectonic plate motion.
- Regional/Local Reference Frames: Such as NAD83 (North America), ETRS89 (Europe), which are tailored to specific continents or countries to account for local geophysical effects.
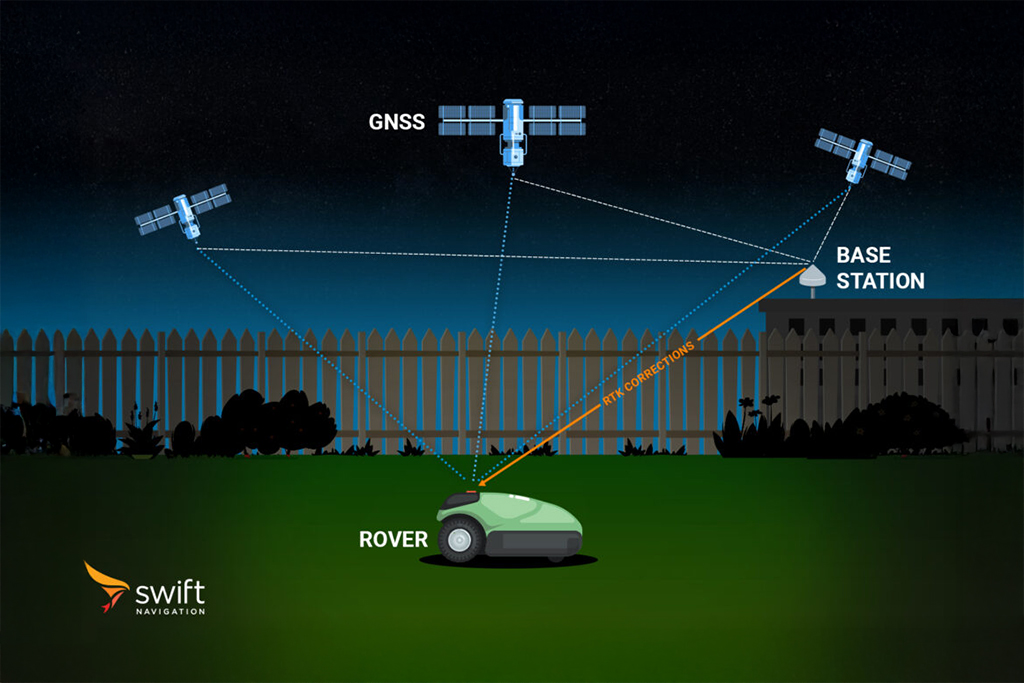
Reference frames are essential for all high-precision GNSS applications. They ensure that positions derived from satellite navigation systems are accurate and compatible worldwide. When using RTK or PPP-RTK services, it’s crucial that both corrections and user positions are referenced to the same frame; otherwise, coordinate transformations must be applied. Reference frames are periodically updated (e.g., ITRF2014 → ITRF2020) to incorporate new data and improve accuracy.
For a more detailed overview of datums, reference frames, and epochs, read our article What Are Reference Frames, Epochs and Coordinate Transformations In RTK?
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan
GIS

Devon Sharp