What is an RTK Baseline?
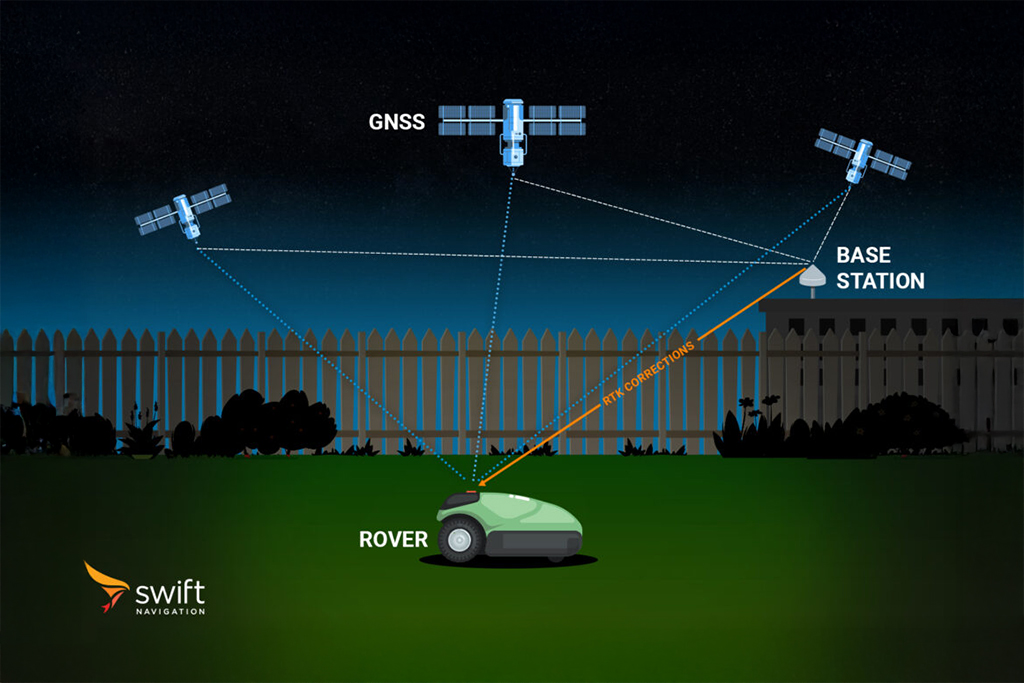
An RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) baseline is the vector distance between two GNSS receivers: a stationary base station and a mobile rover. In essence, it measures the separation between the known reference point and the unknown position you are trying to determine.
How Baselines Affect RTK Performance
Traditional single-baseline RTK relies on one reference station and one rover, and the length of the baseline is the most critical factor influencing accuracy:
- Short Baselines (<10 km): Deliver the highest accuracy, often achieving 1–1.5 cm 2D precision (95% confidence). This is because GNSS signals to both receivers experience nearly identical atmospheric errors, which can be effectively canceled out.
- Long Baselines (>30 km): As the baseline increases, atmospheric effects like ionospheric and tropospheric delays differ between receivers. These errors degrade accuracy and stability. A single-baseline RTK setup may struggle to maintain a fixed solution beyond ~30 km.
To overcome these limitations, network-based RTK approaches such as Network RTK and Virtual Reference Stations (VRS) extend the effective baseline:
- Network RTK combines data from multiple reference stations to model atmospheric effects regionally, enabling centimeter-level accuracy up to 50–70 km.
- VRS generates a “virtual” base station near the rover’s position, keeping the effective baseline short (often <10 km) even when physical station spacing is much larger.
These methods significantly extend RTK’s usable range compared to traditional single-base systems, maintaining accuracy and stability across wider areas.
How RTK Baselines are Measured
An RTK baseline is a vector, meaning it has both length and direction. It can be expressed in different coordinate systems:
- ECEF (Earth-Centered, Earth-Fixed): Measures X, Y, and Z components of the vector from the base to the rover.
- NED (North-East-Down): Measures the relative rover position on a local tangent plane.
Note: Some RTK systems may report a baseline that does not directly equal the physical distance between receivers.
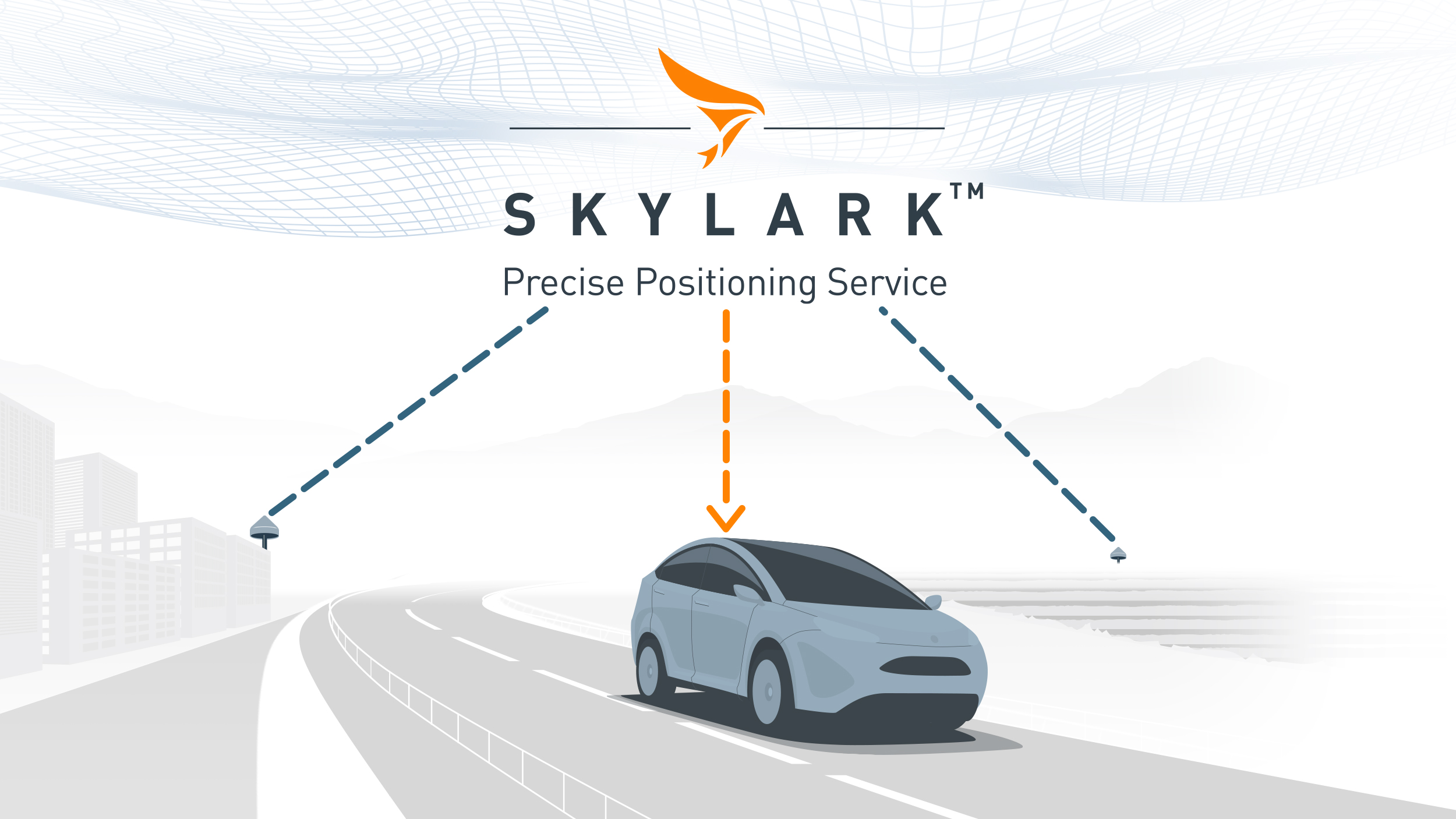
Swift Navigation’s Approach
Swift Navigation extends the performance of RTK beyond the limits of single-baseline systems. Our Skylark™ Nx RTK atmospheric modeling technology supports effective baselines of up to 70 km with ~5 cm accuracy. This extended baseline reduces operational costs and enables affordable, wide-area coverage for reliable precise positioning at scale.
Related Content
GNSS Basics

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan

Devon Sharp

Marwan Ramadan
GIS

Devon Sharp

Devon Sharp
ROBOTICS

Marwan Ramadan